Introduction
Dans une précédente série de blogposts
- Installer Pi OS
- Compilation croisée de Qt 5.15 pour Raspberry Compute Module 4 sur Ubuntu 20 LTS.
- Configurer Qt Creator sur Ubuntu 20 LTS pour la compilation croisée
J'ai écrit sur l'installation de Raspbian sur Raspberry Compute Module et la configuration de la compilation croisée pour QtCreator sur Ubuntu 20.
Cet article est une mise à jour de la version 6.8 de Qt, raspi OS Bookworm et Ubuntu 22.04 LTS.
Conditions préalables
J'ai utilisé le matériel et les logiciels suivants :
- Raspberry Pi 4
- raspi OS Bookworm, sans logiciel recommandé
- Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- Qt 6.8
- QtCreator 14.02
Notes
Si vous disposez d'un ordinateur portable ou de bureau avec suffisamment de mémoire vive et de cœurs de processeur, vous pouvez effectuer la compilation croisée dans une machine virtuelle. Mais j'ai fait l'expérience qu'un ordinateur natif est beaucoup plus rapide et produit moins d'erreurs.
Jetez un coup d'œil aux chemins d'accès aux fichiers et aux adresses IP dans mes exemples de code et adaptez-les à vos besoins.
Configuration du Raspberry Pi
- Télécharger raspiOS à partir de https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/operating-systems
- 2024-07-04-raspios-bookworm-arm64.img.xz : 64bit avec Raspberry Pi OS avec bureau (pas avec le logiciel recommandé)
- Flasher l'image sur la carte SD avec Balena Etcher
- Suivre l'installation et ne pas oublier les paramètres de connexion à distance (ssh)
- Se connecter au RPi avec ssh -> dans mon cas à l'adresse IP 192.168.2.167 et à l'utilisateur pi -> depuis votre hôte Ubuntu
ssh pi@192.168.2.167- Installer les logiciels nécessaires :
sudo apt-get install libboost-all-dev libudev-dev libinput-dev libts-dev libmtdev-dev libjpeg-dev libfontconfig1-dev libssl-dev libdbus-1-dev libglib2.0-dev libxkbcommon-dev libegl1-mesa-dev libgbm-dev libgles2-mesa-dev mesa-common-dev libasound2-dev libpulse-dev gstreamer1.0-omx libgstreamer1.0-dev libgstreamer-plugins-base1.0-dev gstreamer1.0-alsa libvpx-dev libsrtp2-dev libsnappy-dev libnss3-dev "^libxcb.*" flex bison libxslt-dev ruby gperf libbz2-dev libcups2-dev libatkmm-1.6-dev libxi6 libxcomposite1 libfreetype6-dev libicu-dev libsqlite3-dev libxslt1-dev sudo apt-get install libavcodec-dev libavformat-dev libswscale-dev libx11-dev freetds-dev libsqlite3-dev libpq-dev libiodbc2-dev firebird-dev libxext-dev libxcb1 libxcb1-dev libx11-xcb1 libx11-xcb-dev libxcb-keysyms1 libxcb-keysyms1-dev libxcb-image0 libxcb-image0-dev libxcb-shm0 libxcb-shm0-dev libxcb-icccm4 libxcb-icccm4-dev libxcb-sync1 libxcb-sync-dev libxcb-render-util0 libxcb-render-util0-dev libxcb-xfixes0-dev libxrender-dev libxcb-shape0-dev libxcb-randr0-dev libxcb-glx0-dev libxi-dev libdrm-dev libxcb-xinerama0 libxcb-xinerama0-dev libatspi2.0-dev libxcursor-dev libxcomposite-dev libxdamage-dev libxss-dev libxtst-dev libpci-dev libcap-dev libxrandr-dev libdirectfb-dev libaudio-dev libxkbcommon-x11-dev gdbserver- Créer un dossier pour l'installation de Qt 6 :
sudo mkdir /usr/local/qt6- Découvrir les versions de gcc, ld et ldd. Le code source de la même version doit être téléchargé pour construire le compilateur croisé plus tard.
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ gcc --version
gcc (Debian 12.2.0-14) 12.2.0
Copyright (C) 2022 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. There is NO
warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ ld --version
GNU ld (GNU Binutils for Debian) 2.40
Copyright (C) 2023 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This program is free software; you may redistribute it under the terms of
the GNU General Public License version 3 or (at your option) a later version.
This program has absolutely no warranty.
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ ldd --version
ldd (Debian GLIBC 2.36-9+rpt2+deb12u8) 2.36
Copyright (C) 2022 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
This is free software; see the source for copying conditions. There is NO
warranty; not even for MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Written by Roland McGrath and Ulrich Drepper.- Ajouter le morceau de code suivant à la fin de ~/.bashrc et mettre à jour les changements :
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/qt6/lib/
source ~/.bashrcInstallation d'Ubuntu 22.04 LTS
- Mise à jour des dernières versions des progiciels :
sudo apt update
sudo apt upgrade- Installer les paquets suivants :
sudo apt-get install make build-essential libclang-dev ninja-build gcc git bison python3 gperf pkg-config libfontconfig1-dev libfreetype6-dev libx11-dev libx11-xcb-dev libxext-dev libxfixes-dev libxi-dev libxrender-dev libxcb1-dev libxcb-glx0-dev libxcb-keysyms1-dev libxcb-image0-dev libxcb-shm0-dev libxcb-icccm4-dev libxcb-sync-dev libxcb-xfixes0-dev libxcb-shape0-dev libxcb-randr0-dev libxcb-render-util0-dev libxcb-util-dev libxcb-xinerama0-dev libxcb-xkb-dev libxkbcommon-dev libxkbcommon-x11-dev libatspi2.0-dev libgl1-mesa-dev libglu1-mesa-dev freeglut3-dev build-essential gawk git texinfo bison file wget libssl-dev gdbserver gdb-multiarch libxcb-cursor-devConstruire la dernière version de cmake à partir des sources :
cd ~
wget https://github.com/Kitware/CMake/releases/download/v3.30.5/cmake-3.30.5.tar.gz
tar -xzvf cmake-3.30.5.tar.gz
cd cmake-3.30.5
./bootstrap
make -j$(nproc)
sudo make install
# Update PATH Environment Variable
which cmake
/usr/local/bin/cmake
export PATH=/usr/local/bin/cmake:$PATH
source ~/.bashrc
cmake --versionConstruire gcc en tant que compilateur croisé
Télécharger le code source nécessaire. Vous devez modifier les commandes suivantes en fonction de vos besoins. Au moment où je rédige cette page, elles sont les suivantes :
- gcc 12.2.0
- binutils 2.40 (version ld)
- glibc 2.36(version ldd)
cd ~
mkdir gcc_all && cd gcc_all
wget https://ftpmirror.gnu.org/binutils/binutils-2.40.tar.bz2
wget https://ftpmirror.gnu.org/glibc/glibc-2.36.tar.bz2
wget https://ftpmirror.gnu.org/gcc/gcc-12.2.0/gcc-12.2.0.tar.gz
git clone --depth=1 https://github.com/raspberrypi/linux
tar xf binutils-2.40.tar.bz2
tar xf glibc-2.36.tar.bz2
tar xf gcc-12.2.0.tar.gz
rm *.tar.*
cd gcc-12.2.0
contrib/download_prerequisites- Créer un dossier pour l'installation du compilateur.
sudo mkdir -p /opt/cross-pi-gcc
sudo chown $USER /opt/cross-pi-gcc
export PATH=/opt/cross-pi-gcc/bin:$PATH- Copier les en-têtes du noyau dans le dossier ci-dessus.
cd ~/gcc_all
cd linux
KERNEL=kernel7
make ARCH=arm64 INSTALL_HDR_PATH=/opt/cross-pi-gcc/aarch64-linux-gnu headers_install- Construire Binutils.
cd ~/gcc_all
mkdir build-binutils && cd build-binutils
../binutils-2.40/configure --prefix=/opt/cross-pi-gcc --target=aarch64-linux-gnu --with-arch=armv8 --disable-multilib
make -j 8
make install- Editer gcc-12.2.0/libsanitizer/asan/asan_linux.cpp. Ajouter le morceau de code suivant.
#ifndef PATH_MAX
#define PATH_MAX 4096
#endif- Faire une compilation partielle de gcc.
cd ~/gcc_all
mkdir build-gcc && cd build-gcc
../gcc-12.2.0/configure --prefix=/opt/cross-pi-gcc --target=aarch64-linux-gnu --enable-languages=c,c++ --disable-multilib
make -j8 all-gcc
make install-gcc- Compilation partielle de la Glibc.
cd ~/gcc_all
mkdir build-glibc && cd build-glibc
../glibc-2.36/configure --prefix=/opt/cross-pi-gcc/aarch64-linux-gnu --build=$MACHTYPE --host=aarch64-linux-gnu --target=aarch64-linux-gnu --with-headers=/opt/cross-pi-gcc/aarch64-linux-gnu/include --disable-multilib libc_cv_forced_unwind=yes
make install-bootstrap-headers=yes install-headers
make -j8 csu/subdir_lib
install csu/crt1.o csu/crti.o csu/crtn.o /opt/cross-pi-gcc/aarch64-linux-gnu/lib
aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc -nostdlib -nostartfiles -shared -x c /dev/null -o /opt/cross-pi-gcc/aarch64-linux-gnu/lib/libc.so
touch /opt/cross-pi-gcc/aarch64-linux-gnu/include/gnu/stubs.h- Retour à gcc.
cd ~/gcc_all/build-gcc
make -j8 all-target-libgcc
make install-target-libgcc- Finir la construction de la glibc.
cd ~/gcc_all/build-glibc
make -j8
make install- Finir la construction de gcc.
cd ~/gcc_all/build-gcc
make -j8
make installA ce stade, nous avons une chaîne d'outils complète de compilateur croisé avec gcc. Le dossier gcc_all n'est plus nécessaire. Vous pouvez le supprimer.
Construire Qt6
Il y a deux possibilités pour construire Qt6. Il existe une version "single" (https://download.qt.io/official_releases/qt/6.8/6.8.0/single/qt-everywhere-src-6.8.0.tar.xz) à télécharger, qui contient qtbase et tous les sous-modules. Cette version est très lourde et nécessite beaucoup de puissance et de temps pour la compiler.
Je recommande de compiler qtbase comme base et de ne compiler ensuite que chaque sous-module dont vous avez besoin séparément.
- Créer des dossiers pour sysroot et qt6. Je crée ces dossiers dans le répertoire workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation.
cd ~/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation
mkdir rpi-sysroot rpi-sysroot/usr rpi-sysroot/opt
mkdir qt6 qt6/host qt6/pi qt6/host-build qt6/pi-build qt6/src- Télécharger le code source de QtBase
cd ~/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/qt6/src
wget https://download.qt.io/official_releases/qt/6.8/6.8.0/submodules/qtbase-everywhere-src-6.8.0.tar.xz
tar xf qtbase-everywhere-src-6.8.0.tar.xzConstruire Qt6 pour l'hôte
cd ~/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/qt6/host-build/
cmake ../src/qtbase-everywhere-src-6.8.0/ -GNinja -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DQT_BUILD_EXAMPLES=OFF -DQT_BUILD_TESTS=OFF -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=$HOME/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/qt6/host
cmake --build . --parallel 8
cmake --install .Les binaires seront dans ~/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/qt6/host
Construire Qt6 pour rpi
Copier et coller quelques dossiers de rpi en utilisant rsync via SSH.
cd ~
rsync -avz --rsync-path="sudo rsync" pi@192.168.2.167:/usr/include workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/rpi-sysroot/usr
rsync -avz --rsync-path="sudo rsync" pi@192.168.2.167:/lib workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/rpi-sysroot
rsync -avz --rsync-path="sudo rsync" pi@192.168.2.167:/usr/lib workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/rpi-sysroot/usr
rsync -avz --rsync-path="sudo rsync" pi@192.168.2.167:/opt/vc workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/rpi-sysroot/opt- Créez un fichier nommé toolchain.cmake dans ~/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/qt6.
Vous devez ajuster la ligne "set(TARGET_SYSROOT /home/factory/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/rpi-sysroot)" à votre environnement.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.18)
include_guard(GLOBAL)
set(CMAKE_SYSTEM_NAME Linux)
set(CMAKE_SYSTEM_PROCESSOR arm)
# You should change location of sysroot to your needs.
set(TARGET_SYSROOT /home/factory/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/rpi-sysroot)
set(TARGET_ARCHITECTURE aarch64-linux-gnu)
set(CMAKE_SYSROOT ${TARGET_SYSROOT})
set(ENV{PKG_CONFIG_PATH} $PKG_CONFIG_PATH:${CMAKE_SYSROOT}/usr/lib/${TARGET_ARCHITECTURE}/pkgconfig)
set(ENV{PKG_CONFIG_LIBDIR} /usr/lib/pkgconfig:/usr/share/pkgconfig/:${TARGET_SYSROOT}/usr/lib/${TARGET_ARCHITECTURE}/pkgconfig:${TARGET_SYSROOT}/usr/lib/pkgconfig)
set(ENV{PKG_CONFIG_SYSROOT_DIR} ${CMAKE_SYSROOT})
set(CMAKE_C_COMPILER /opt/cross-pi-gcc/bin/${TARGET_ARCHITECTURE}-gcc)
set(CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER /opt/cross-pi-gcc/bin/${TARGET_ARCHITECTURE}-g++)
set(CMAKE_C_FLAGS "${CMAKE_C_FLAGS} -isystem=/usr/include -isystem=/usr/local/include -isystem=/usr/include/${TARGET_ARCHITECTURE}")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_C_FLAGS}")
set(QT_COMPILER_FLAGS "-march=armv8-a")
set(QT_COMPILER_FLAGS_RELEASE "-O2 -pipe")
set(QT_LINKER_FLAGS "-Wl,-O1 -Wl,--hash-style=gnu -Wl,--as-needed -Wl,-rpath-link=${TARGET_SYSROOT}/usr/lib/${TARGET_ARCHITECTURE} -Wl,-rpath-link=$HOME/qt6/pi/lib")
set(CMAKE_FIND_ROOT_PATH_MODE_PROGRAM NEVER)
set(CMAKE_FIND_ROOT_PATH_MODE_LIBRARY ONLY)
set(CMAKE_FIND_ROOT_PATH_MODE_INCLUDE ONLY)
set(CMAKE_FIND_ROOT_PATH_MODE_PACKAGE ONLY)
set(CMAKE_INSTALL_RPATH_USE_LINK_PATH TRUE)
set(CMAKE_BUILD_RPATH ${TARGET_SYSROOT})
include(CMakeInitializeConfigs)
function(cmake_initialize_per_config_variable _PREFIX _DOCSTRING)
if (_PREFIX MATCHES "CMAKE_(C|CXX|ASM)_FLAGS")
set(CMAKE_${CMAKE_MATCH_1}_FLAGS_INIT "${QT_COMPILER_FLAGS}")
foreach (config DEBUG RELEASE MINSIZEREL RELWITHDEBINFO)
if (DEFINED QT_COMPILER_FLAGS_${config})
set(CMAKE_${CMAKE_MATCH_1}_FLAGS_${config}_INIT "${QT_COMPILER_FLAGS_${config}}")
endif()
endforeach()
endif()
if (_PREFIX MATCHES "CMAKE_(SHARED|MODULE|EXE)_LINKER_FLAGS")
foreach (config SHARED MODULE EXE)
set(CMAKE_${config}_LINKER_FLAGS_INIT "${QT_LINKER_FLAGS}")
endforeach()
endif()
_cmake_initialize_per_config_variable(${ARGV})
endfunction()
set(XCB_PATH_VARIABLE ${TARGET_SYSROOT})
set(GL_INC_DIR ${TARGET_SYSROOT}/usr/include)
set(GL_LIB_DIR ${TARGET_SYSROOT}:${TARGET_SYSROOT}/usr/lib/${TARGET_ARCHITECTURE}/:${TARGET_SYSROOT}/usr:${TARGET_SYSROOT}/usr/lib)
set(EGL_INCLUDE_DIR ${GL_INC_DIR})
set(EGL_LIBRARY ${XCB_PATH_VARIABLE}/usr/lib/${TARGET_ARCHITECTURE}/libEGL.so)
set(OPENGL_INCLUDE_DIR ${GL_INC_DIR})
set(OPENGL_opengl_LIBRARY ${XCB_PATH_VARIABLE}/usr/lib/${TARGET_ARCHITECTURE}/libOpenGL.so)
set(GLESv2_INCLUDE_DIR ${GL_INC_DIR})
set(GLIB_LIBRARY ${XCB_PATH_VARIABLE}/usr/lib/${TARGET_ARCHITECTURE}/libGLESv2.so)
set(GLESv2_INCLUDE_DIR ${GL_INC_DIR})
set(GLESv2_LIBRARY ${XCB_PATH_VARIABLE}/usr/lib/${TARGET_ARCHITECTURE}/libGLESv2.so)
set(gbm_INCLUDE_DIR ${GL_INC_DIR})
set(gbm_LIBRARY ${XCB_PATH_VARIABLE}/usr/lib/${TARGET_ARCHITECTURE}/libgbm.so)
set(Libdrm_INCLUDE_DIR ${GL_INC_DIR})
set(Libdrm_LIBRARY ${XCB_PATH_VARIABLE}/usr/lib/${TARGET_ARCHITECTURE}/libdrm.so)
set(XCB_XCB_INCLUDE_DIR ${GL_INC_DIR})
set(XCB_XCB_LIBRARY ${XCB_PATH_VARIABLE}/usr/lib/${TARGET_ARCHITECTURE}/libxcb.so)
list(APPEND CMAKE_LIBRARY_PATH ${CMAKE_SYSROOT}/usr/lib/${TARGET_ARCHITECTURE})
list(APPEND CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH "/usr/lib/${TARGET_ARCHITECTURE}/cmake")- Correction des liens symboliques absolus
cd ~/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/riscv/riscv-poky/master/scripts/sysroot-relativelinks.py
chmod +x sysroot-relativelinks.py
python3 sysroot-relativelinks.py rpi-sysroot- Compilation du code source pour rpi.
cd $HOME/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/qt6/pi-build
cmake ../src/qtbase-everywhere-src-6.8.0/ -GNinja -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DINPUT_opengl=es2 -DQT_BUILD_EXAMPLES=OFF -DQT_BUILD_TESTS=OFF -DQT_HOST_PATH=$HOME/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/qt6/host -DCMAKE_STAGING_PREFIX=$HOME/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/qt6/pi -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local/qt6 -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE=$HOME/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/qt6/toolchain.cmake -DQT_QMAKE_TARGET_MKSPEC=devices/linux-rasp-pi4-aarch64 -DQT_FEATURE_xcb=ON -DFEATURE_xcb_xlib=ON -DQT_FEATURE_xlib=ON
cmake --build . --parallel 8
cmake --install .- Envoyer les binaires à rpi.
rsync -avz --rsync-path="sudo rsync" $HOME/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/qt6/pi/* pi@192.168.2.167:/usr/local/qt6Configurer QtCreator
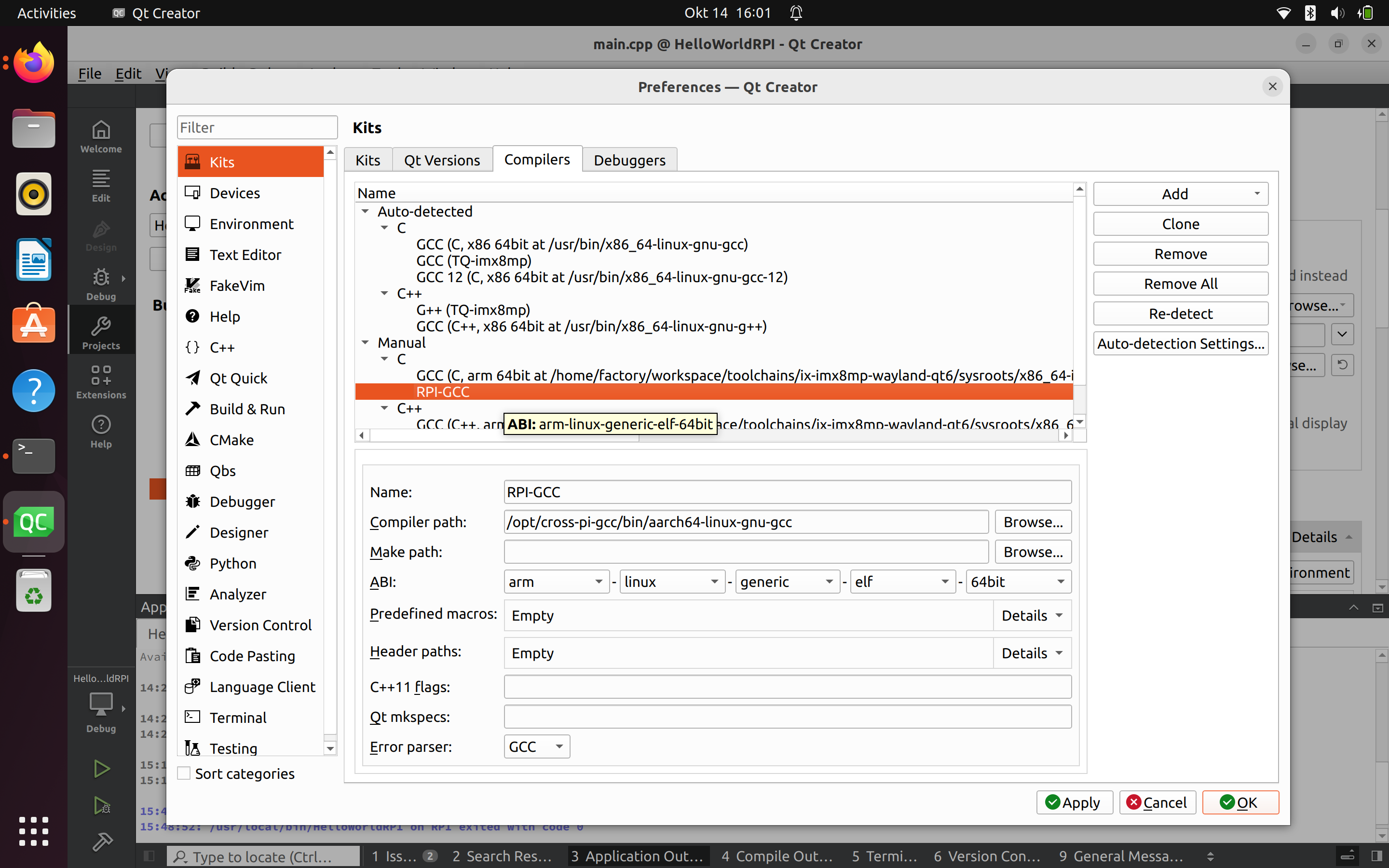
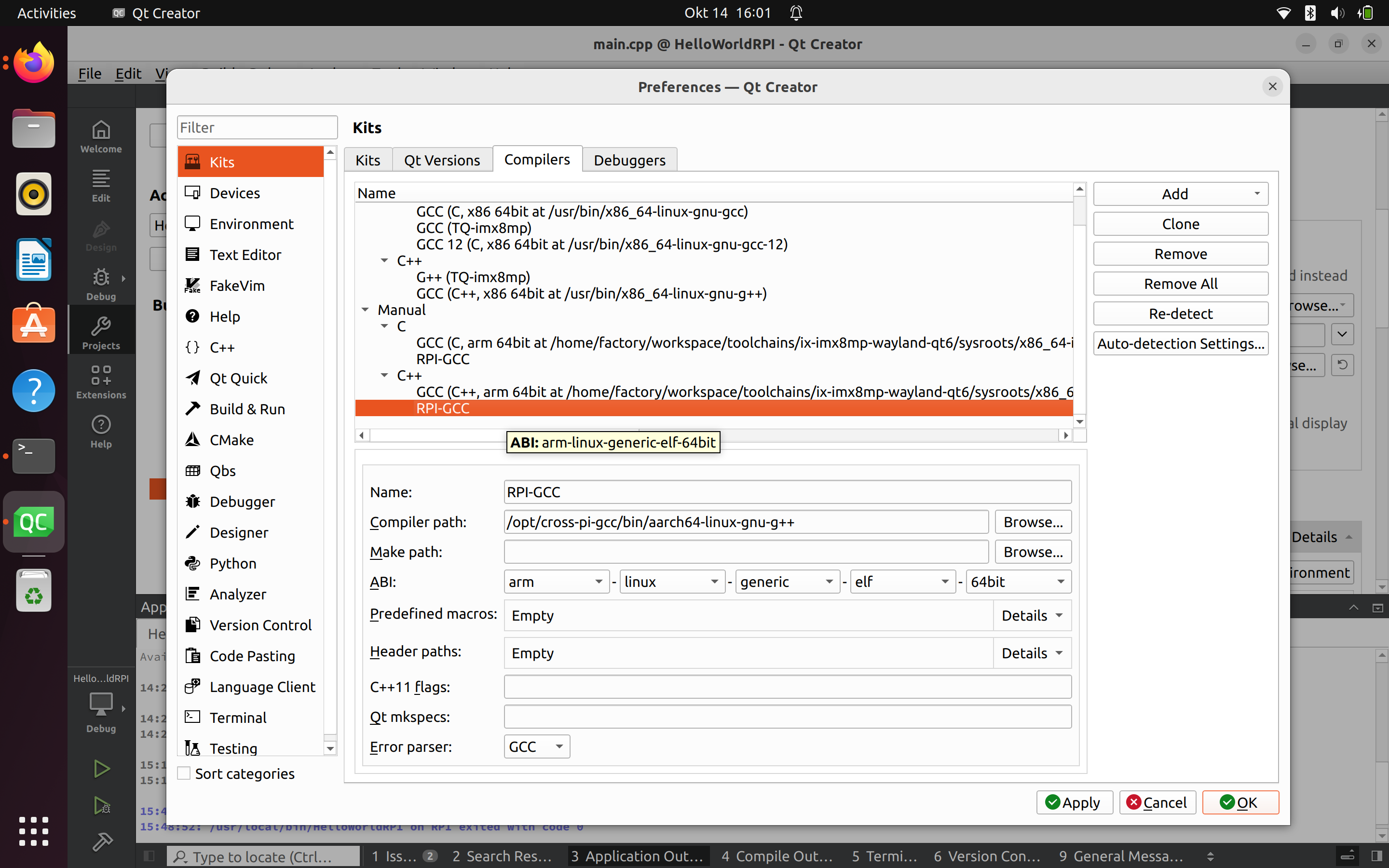
Mise en place de compilateurs
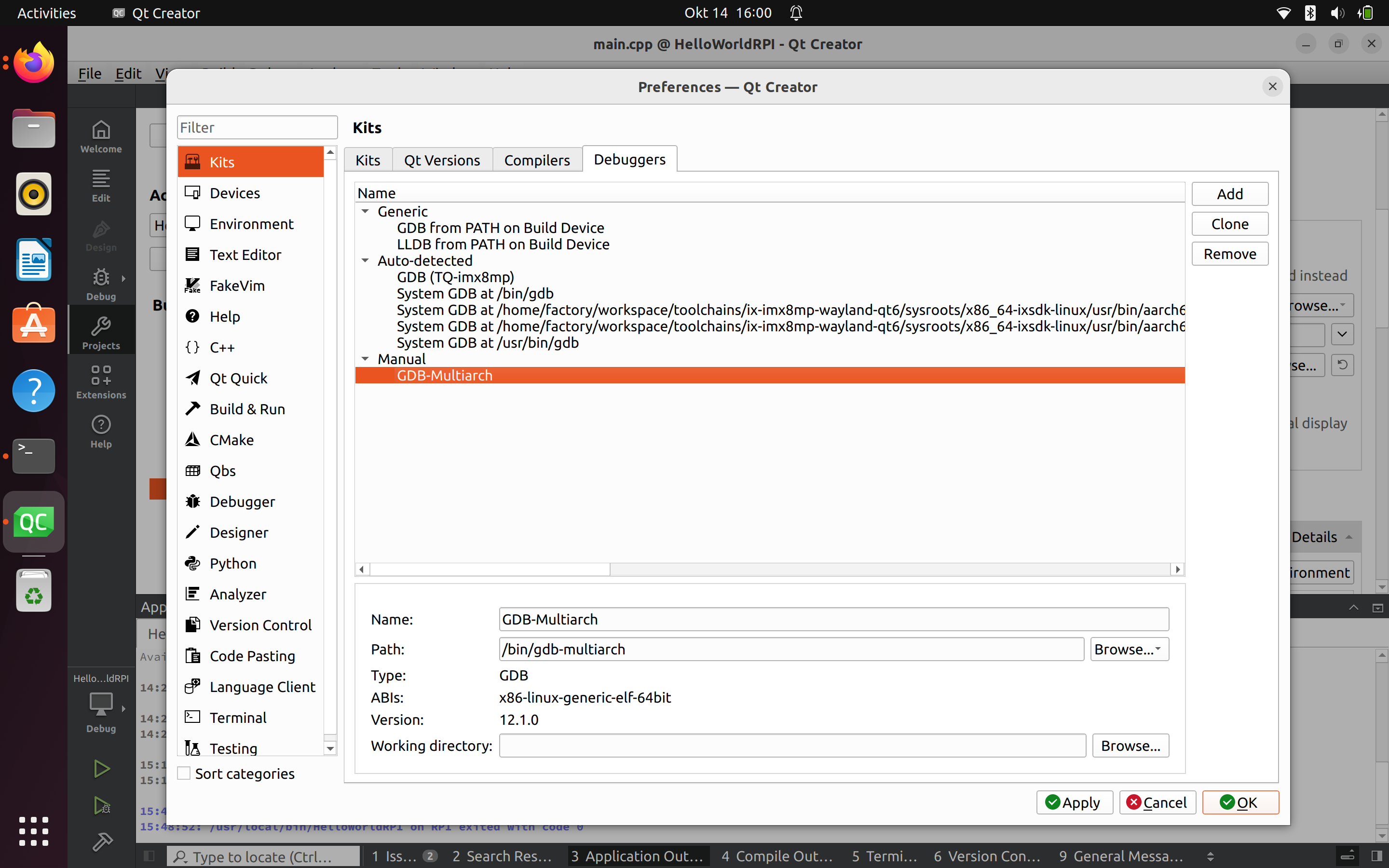
Configurer les débogueurs
Configurer les appareils
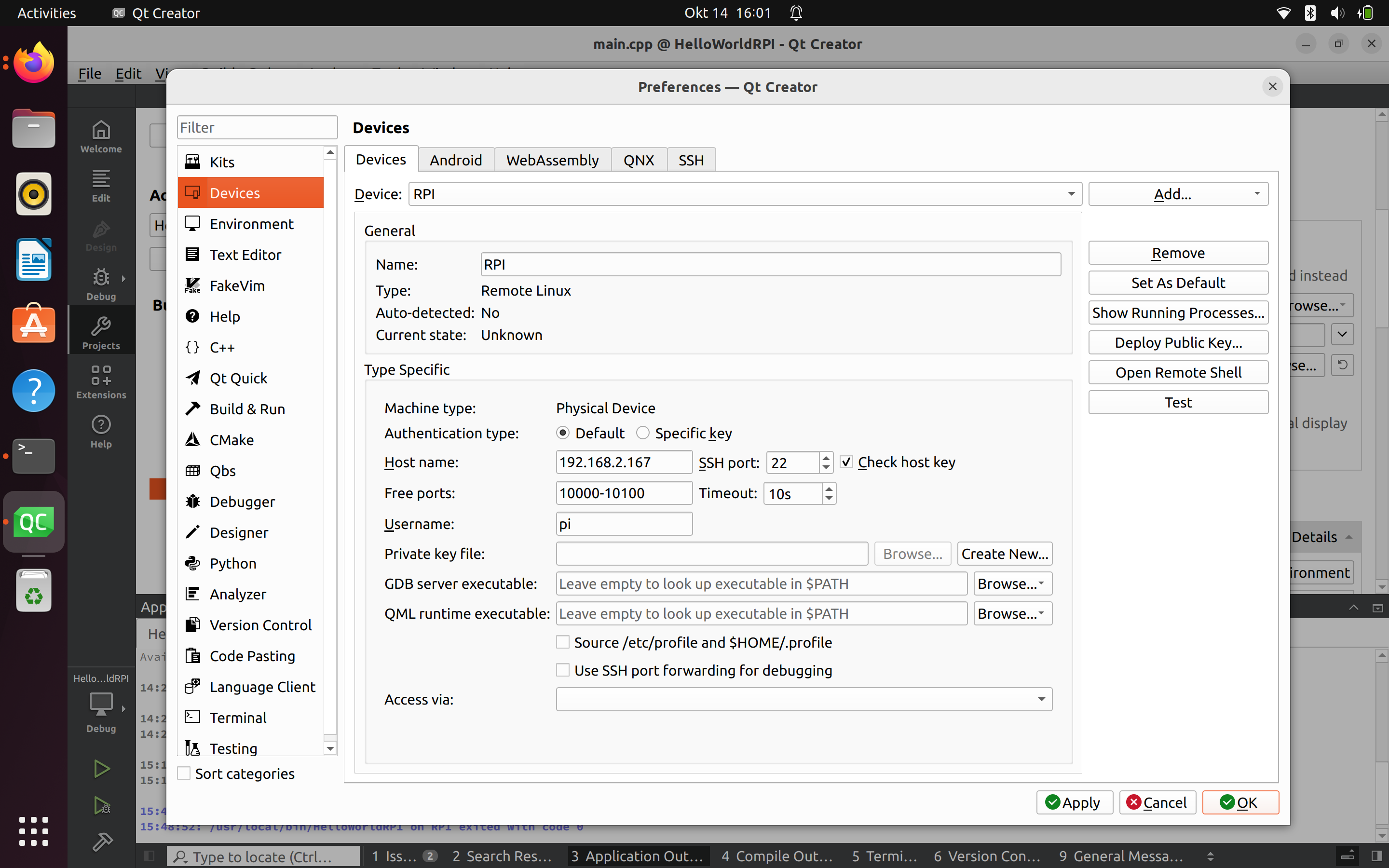
Tester la connexion avec le bouton "Test"Configurer les versions de Qt
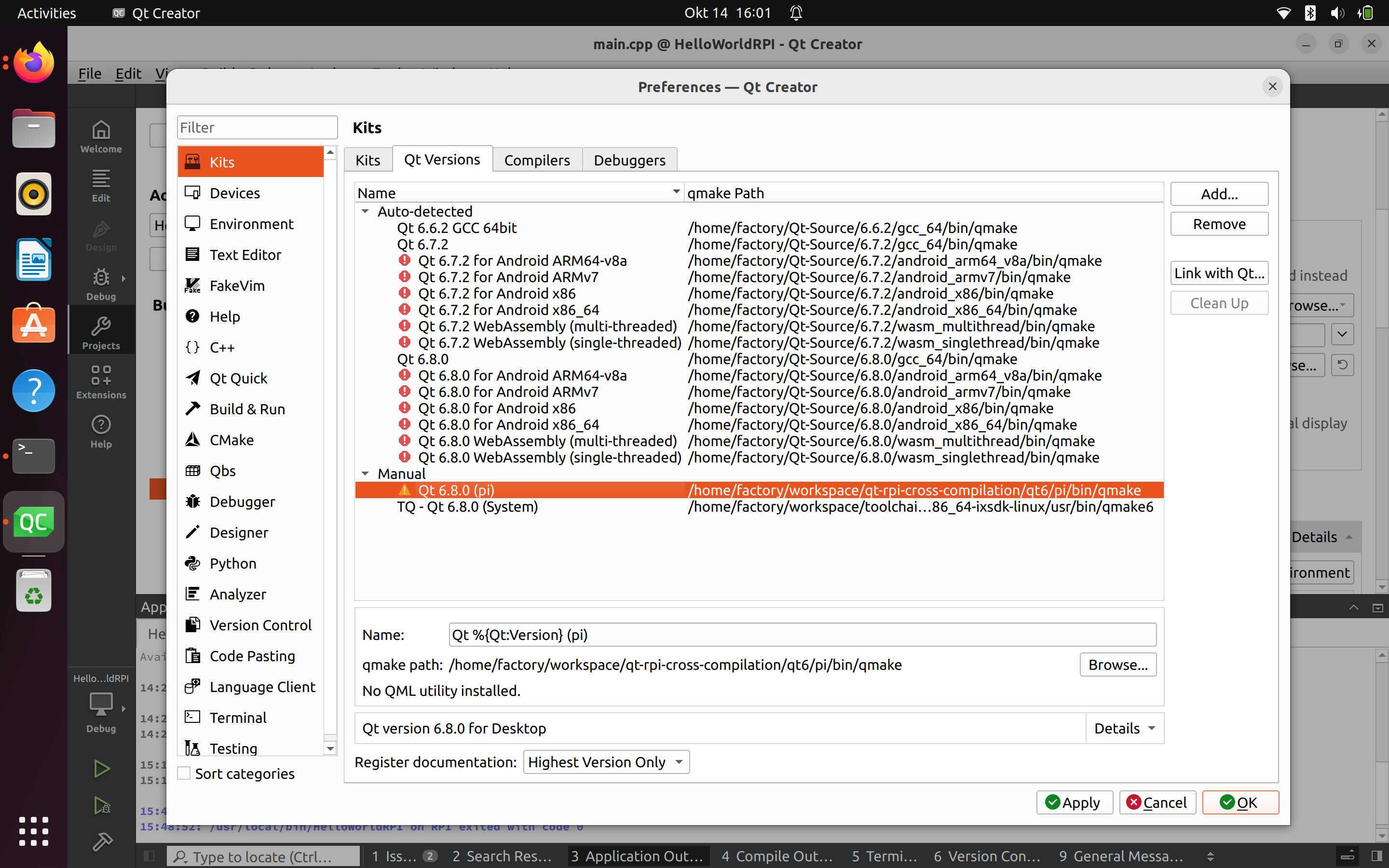
Configurer les kits
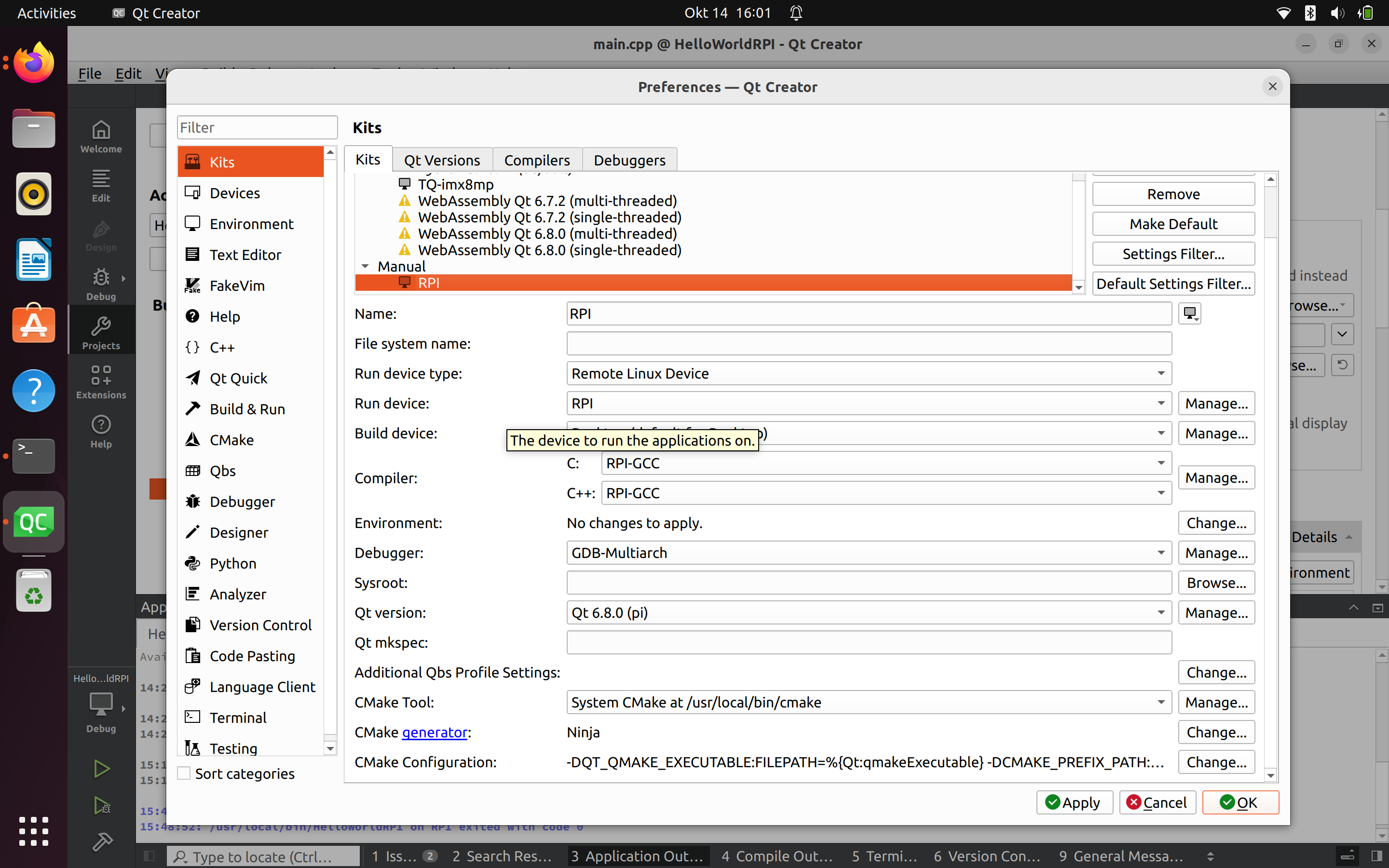
Dans "CMake Configuration", cliquez sur Change et ajoutez les commandes suivantes.
-DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE:UNINITIALIZED=/home/pmy/qt6/pi/lib/cmake/Qt6/qt.toolchain.cmakeParamètres du projet QtCreator
Si vous créez un projet dans QtCreator, vous devez ajuster la configuration de "Run". Sur "Environment", vous devez ajouter :
-LD_LIBRARY_PATH=:/usr/local/qt6/lib/Ajouter des sous-modules Qt
Ajouter le module QML
- Télécharger les codes sources :
cd ~/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/qt6/src
wget https://download.qt.io/official_releases/qt/6.8/6.8.0/submodules/qtshadertools-everywhere-src-6.8.0.tar.xz
tar xf qtshadertools-everywhere-src-6.8.0.tar.xz
wget https://download.qt.io/official_releases/qt/6.8/6.8.0/submodules/qtdeclarative-everywhere-src-6.8.0.tar.xz
tar xf qtdeclarative-everywhere-src-6.8.0.tar.xzVous devez vérifier les dépendances à ~/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/qt6/src/qtdeclarative-everywhere-src-6.8.0/dependencies.yaml et ~/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/qt6/src/qtshadertools-everywhere-src-6.8.0/dependencies.yaml.
Assurez-vous que les modules requis soient construits et installés en premier.
- Construire les modules pour l'hôte.
cd ~/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/qt6/host-build
rm -rf *
$HOME/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/qt6/host/bin/qt-configure-module ../src/qtshadertools-everywhere-src-6.8.0
cmake --build . --parallel 8
cmake --install .
rm -rf *
$HOME/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/qt6/host/bin/qt-configure-module ../src/qtdeclarative-everywhere-src-6.8.0
cmake --build . --parallel 8
cmake --install .- Construire les modules pour rpi
cd ~/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/qt6/pi-build
rm -rf *
$HOME/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/qt6/pi/bin/qt-configure-module ../src/qtshadertools-everywhere-src-6.8.0
cmake --build . --parallel 8
cmake --install .
rm -rf *
$HOME/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/qt6/pi/bin/qt-configure-module ../src/qtdeclarative-everywhere-src-6.8.0
cmake --build . --parallel 8
cmake --install .- Envoyer les binaires à rpi.
rsync -avz --rsync-path="sudo rsync" $HOME/workspace/qt-rpi-cross-compilation/qt6/pi/* pi@192.168.2.167:/usr/local/qt6Remerciements
Sources utilisées pour l'élaboration de cette instruction :
- https://wiki.qt.io/Cross-Compile_Qt_6_for_Raspberry_Pi
- https://github.com/MuyePan/CrossCompileQtForRpi
Merci à tous.