Carbon nanobuds (CNB) were discovered in 2006 by the founders of the Finnish company Canatu Oy when the research group was trying to produce single-walled carbon nanotubes. CNBs are therefore a combination of carbon nanotubes and spherical fullerenes (hollow, closed molecules of carbon atoms) and combine properties of both materials.
Alternative to ITO
CNB has a high electrical as well as thermal conductivity, is mechanically very stable with low density at the same time. Like fullerenes, CNBs are highly reactive. Randomly oriented nanobuds show low working function and chemical functionalizability. CNBs are semiconducting and therefore particularly interesting for use in electrical engineering.
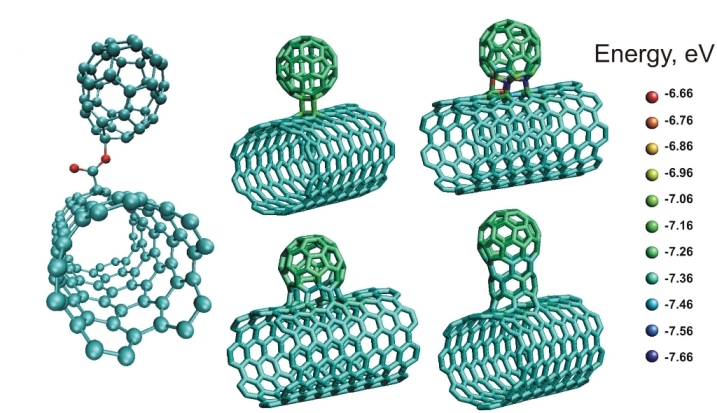
#### Image source: Computer models of some stable nanobud structures (Wikipedia, Arkady Krasheninnikov)
CNB can be seen as an alternative to ITO (indium tin oxide) because, according to Canatu, it is produced under normal pressure at room temperature in a more cost-effective and environmentally friendly way. In contrast to ITO, which can only be produced in a vacuum.